Keywords
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography, non-tuberculous mycobacterium, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Abstract
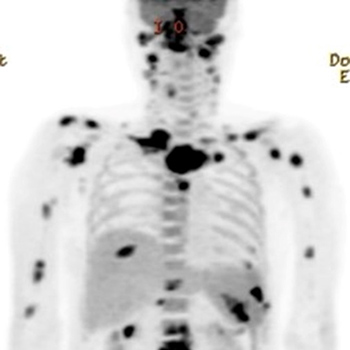
Fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/ computed tomography (18FDG-PET/CT) has been used to diagnose vasculitis, tuberculosis and malignancy. Because PET/CT scan show hotspots during an activation of clinically suspected lesions, it is widely used for diagnosis. However, there are rare cases of PET/CT images for vasculitis combined with tuberculosis. Here we report a case of an eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis in a patient with disseminated non-tuberculosis mycobacterial infection in multiple sites mimicking metastatic malignacy and describe the associated PET/CT scan findings before and after treatment.
References
Views: 910
HTML downloads: 90
PDF downloads: 381
Published:
2019-11-22
Issue:
Vol 6 No 12
(view)










