Keywords
Phentermine, Takotsubo disease, lisdexamfetamine, sympathetic overstimulation
Abstract
Objectives: This is the first case report of iatrogenic Takotsubo syndrome (TS) due to a combination of lisdexamfetamine and phentermine.
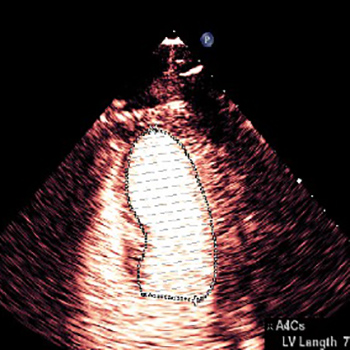
Background: TS is characterized by transient acute ballooning of the left ventricular wall. Typically, it occurs in extremely stressed post-menopausal women, however a few iatrogenic causes have been described recently.
Results: A 55-year old woman prescribed lisdexamfetamine and phentermine, presented with acute substernal chest pain. Acute coronary syndrome was excluded. The echocardiogram was diagnostic of TS, and she recovered spontaneously, with supportive care.
Conclusion: Caution with the use of sympathomimetic medications in post-menopausal women appears warranted.
References