Keywords
COVID-19, C-reactive protein, D-dimer, pulmonary embolism
Abstract
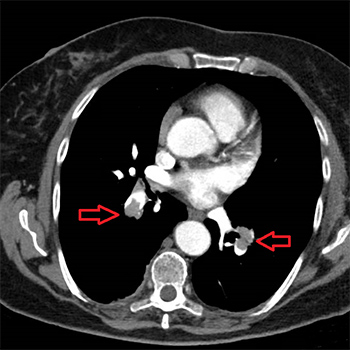
The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is challenging in symptomatic COVID-19 patients since shortness of breath, chest pain, tachycardia, tachypnoea, fever, oxygen desaturation and high D-dimer blood levels might be features of both diseases. We present two COVID-19 patients in whom pulmonary embolism was suspected (and diagnosed) due to a discrepancy between an increase in D-dimer blood levels and a decrease in C-reactive protein blood levels over time. We believe that an opposite change in the blood levels of both biomarkers over time may be used as a novel method to predict pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 patients.
References
Views: 1722
HTML downloads: 1328
PDF downloads: 831
Published:
2020-05-20
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 6
(view)










