Keywords
Contarini’s syndrome, bilateral pleural effusion, rheumatoid arthritis, pseudochylothorax, rheumatoid pleuritis
Abstract
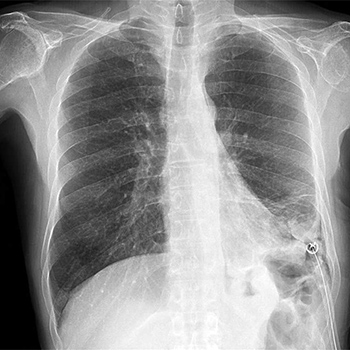
A 67-year-old man with a history of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was admitted to the Internal Medicine ward for bilateral pleural effusion. Two years before this episode, coinciding with an exacerbation of the RA, he was incidentally diagnosed with asymptomatic left pleural effusion compatible with rheumatoid exudate, which was resolved with a tube thoracostomy. Three weeks before admission, the patient developed asthenia, orthopnoea and progressive dyspnoea. A chest x-ray revealed bilateral pleural effusion occupying the lower third of the left hemithorax and a smaller portion of the right hemithorax along with marked elevation of N-terminal fragment of pro-brain natriuretic peptide levels. The patient was admitted with a diagnosis of left-sided heart failure. Transthoracic echocardiography and cardiac catheterization confirmed the existence of ischaemic cardiomyopathy. After 2 days of diuretic treatment, the right pleural effusion resolved, but the left effusion persisted. A needle thoracentesis was performed, draining 800 ml of milky fluid compatible with rheumatoid pseudochylothorax.
References