Keywords
Portal vein thrombosis, acute pyelonephritis, type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Background: Few cases have been reported with respect to portal vein thrombosis in non-cirrhotic patients. Asymptomatic or non-specific symptoms of portal vein thrombosis may lead to misdiagnosis or may delay the diagnosis until complications develop. We report a case of portal vein thrombosis in a patient with type 1 diabetes presenting as acute pyelonephritis.
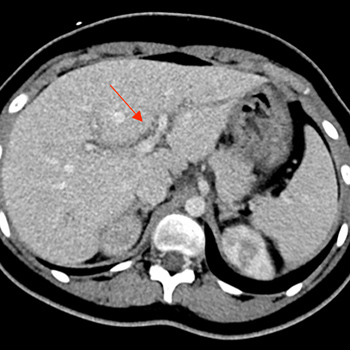
Case description: An 18-year-old female with type 1 diabetes on an insulin pump presented with epigastric abdominal pain for 3 days associated with nausea and vomiting. She was a conscious, alert, young female who appeared to be in pain. Vital signs were stable with a random blood sugar (RBS) level of 179 mg/dl. Abdominal examination revealed a soft and lax abdomen with tenderness in the epigastric area and right renal angle, as well as no sign of rigidity or rebound tenderness. No signs of ascites, splenomegaly or hepatomegaly were noted. Investigations showed a WBC count of 10.2, neutrophils at 65%, urine microsopy analysis revealed WBCs between 30–50 per high power field, with culture showing >105 CFU/ml. All parameters of a thrombophilic screen were within normal values. Computed tomography (CT) revealed reduced enhancement of the right kidney, likely indicating acute pyelonephritis, and left portal vein oedema with complete occlusion. Local factors and prothrombotic disorders were ruled out. The patient was managed with ciprofloxacin, enoxaparin and warfarin. Follow-up imaging revealed complete resolution of thrombosis.
Conclusions:Portal vein thrombosis is an uncommon condition in the absence of liver disease. Few case reports exhibit sepsis and portal vein thrombosis. Sepsis can create a predisposed environment for hypercoagulability. To our knowledge, this is the first case report of pyelonephritis with portal vein thrombosis.
References
Views: 1380
HTML downloads: 124
PDF downloads: 527
Published:
2020-02-05
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 3
(view)










