Keywords
SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, COVID-19, coronavirus, Takotsubo syndrome
Abstract
Objective: The availability of public health information for optimised supportive care is critical during the COVID-19 pandemic. We describe the first case of COVID-19 complicated by Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
Materials and Methods: We report the clinical, laboratory and radiological findings of a patient with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
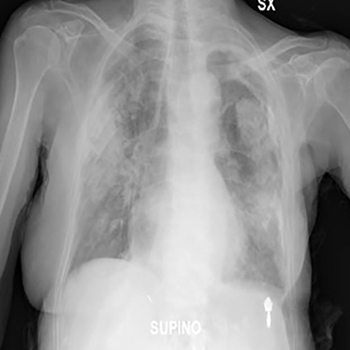
Results: The nasopharyngeal swab was positive for SARS-CoV-2 and x-ray images demonstrated pathognomonic pneumonia. The patient developed tachycardia and the echocardiogram confirmed the diagnosis of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
Conclusions: Doctors should be aware of the need to thoroughly study this new infection in order to understand its underlying mechanisms and related complications.
References