Keywords
Coronavirus, COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, pulmonary embolism, coagulation abnormalities, tocilizumab
Abstract
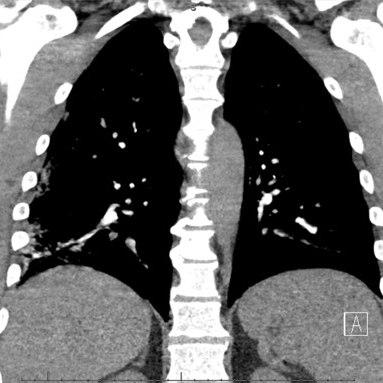
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2 was reported to be responsible for a cluster of acute atypical respiratory pneumonia cases in Wuhan, in Hubei province, China. The disease caused by this virus is called COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019). The virus is transmitted between humans and the outbreak was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on 11 March 2020. Coagulopathy is a common abnormality in patients with COVID?19 due to inflammation, hypoxia, immobilisation, endothelial damage and diffuse intravascular coagulation. However, the data on this topic are still limited. Here we report the case of a man presenting with pneumonia complicated by bilateral pulmonary embolism.
References