Keywords
Osmotic demyelination syndrome, catatonia, hyponatraemia, hyperemesis gravidarum, plasmapheresis
Abstract
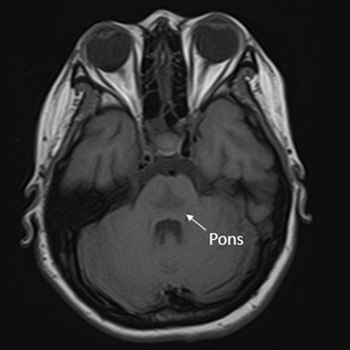
Osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS) is a disorder characterised by the widespread development of demyelination in both pontine and extrapontine regions. It has been recognised as a complication arising from the rapid correction of hyponatraemia. This study presents the case of a 20-year-old Thai female patient at 10 weeks gestation, exhibiting an initial presentation of catatonia – an uncommon manifestation of ODS. The patient developed symptoms following the rapid correction of hyponatraemia in the context of hyperemesis gravidarum. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain revealed a trident or bat-wing-shaped pattern in T2-weighted and fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences at the central pons. The patient underwent five cycles of plasmapheresis and received rehabilitation, leading to clinical improvement.
References
Views: 303
HTML downloads: 38
PDF downloads: 345
Published:
2024-03-11
Issue:
2024: Vol 11 No 4
(view)










