Keywords
5-oxoproline, acetaminophen, flucloxacillin, anion gap, metabolic acidosis
Abstract
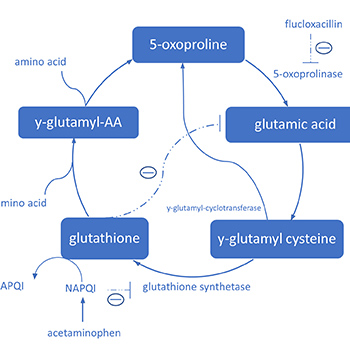
Acetaminophen and flucloxacillin both interfere with the ?-glutamyl cycle. Long-lasting concomitant use of flucloxacillin and acetaminophen can lead to 5-oxoproline accumulation and severe high anion gap metabolic acidosis. Females and patients with sepsis, impaired kidney and/or liver function, malnutrition, advanced age, congenital 5-oxoprolinase deficiency and supratherapeutic acetaminophen and flucloxacillin dosage are associated with increased risk. Therefore, a critical attitude towards the prescription of acetaminophen concomitant with flucloxacillin in these patients is needed.
We present the case of a 79-year-old woman with severe 5-oxoprolinaemia after long-lasting treatment with flucloxacillin and acetaminophen, explaining the toxicological mechanism and risk factors, and we make recommendations for acetaminophen use in patients with long-lasting flucloxacillin treatment.
References
Views: 1138
HTML downloads: 150
PDF downloads: 526
Published:
2020-04-23
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 7
(view)










