Keywords
Intra-cerebral haemorrhage, spontaneous, chest pain, diagnosis
Abstract
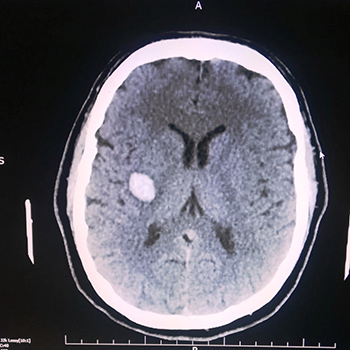
Spontaneous, non-traumatic intra-cerebral haemorrhage is the second most common type of stroke and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality. It is defined as the presence of blood within the cerebral parenchyma without prior injury or surgery. The purpose of this work is to describe an atypical presentation of spontaneous intra-cerebral haemorrhage in a healthy young adult. A literature review was also carried out.
References
Views: 998
HTML downloads: 211
PDF downloads: 605
Published:
2020-07-01
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 9
(view)










