Keywords
Hydorxychloroquine, cardiotoxicity, heart failure, side effect, systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Hydroxychloroquine is an antimalarial drug used in many rheumatologic and systemic diseases. Although considered by clinicians to be relatively safe, serious side effects have been documented (retinotoxicity, neuromyotoxicity and cardiotoxicity).
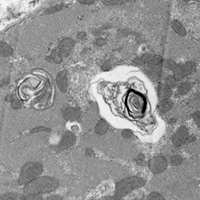
We present the case of a 41-year-old woman with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) who presented at our institution with acute heart failure after taking hydroxychloroquine for a period of 3 months. An endomyocardial biopsy ruled out myocarditis related to systemic lupus erythematosus but demonstrated pathological changes related to hydroxychloroquine toxicity. It is exceptional to observe such cardiac toxicity after such a low cumulative dose (16 grams).
The potential severity and reversibility of this complication underscores the importance of a high level of suspicion and timely diagnosis.
References
Views: 1135
HTML downloads: 1018
PDF downloads: 525
Electron micrograph from right ventricular endomyocardium showing the presence of myeloid bodies downloads: 0
submission downloads: 0
Published:
2015-05-05
Issue:
Vol. 2 No. 3 (2015)
(view)










