Keywords
Pulmonary aspergillosis, chronic granulomatous disease, hypereosinophilia, eosinophilic pneumonia, pulmonary infiltrates with eosinophilia
Abstract
Background: Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a rare immunodeficiency disorder resulting in phagocytic cell dysfunction. It is characterized by deficient cellular immunity against bacteria and fungi, and an excessive inflammatory response resulting in granuloma formation. It manifests, usually in early childhood, with recurrent bacterial and fungal infections or inflammatory complications. The infections, such as invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, can be life-threatening.
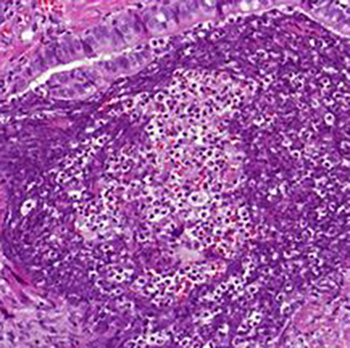
Case description: Our patient was a 40-year-old man with no pulmonary history who presented with bilateral pulmonary nodules and pronounced eosinophilia in peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, mimicking eosinophilic pneumonia. During treatment with corticosteroids, the patient deteriorated clinically and radiographically. Extensive investigations failed to provide a diagnosis. A lung biopsy demonstrated the presence of granulomas and Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae. Advanced screening to detect underlying immunodeficiency revealed CGD.
Discussion: This case report describes a unique first presentation of CGD. It reminds physicians of the possibility of CGD as an underlying immune disorder in invasive aspergillosis and highlights the challenges of diagnosing invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. We discuss the diagnostic pitfalls of this case and propose a diagnostic work-up for eosinophilic lung disease.
References
Views: 545
HTML downloads: 90
PDF downloads: 279
Published:
2022-07-11
Issue:
2022: Vol 9 No 7
(view)










