Keywords
Beau's lines, COVID-19, interleukin-6
Abstract
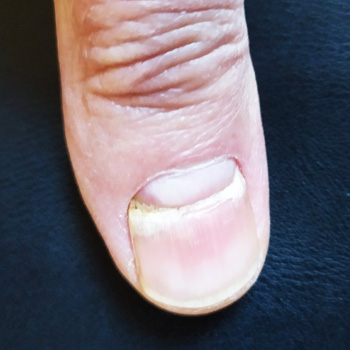
Background: Beau's lines are transverse grooves in the nail plate that result from transient interruption of the growth of the proximal nail matrix. These rare nail disorders can be triggered mostly by infections or systemic diseases.
Case Description: We describe a 65-year-old man who presented with nail changes on all fingernails. The patient, a non-smoker with no medication history, had severe immune responses during two hospitalisations, 9 and 4 months ago, for COVID-19. Both hospitalisations were accompanied by markedly elevated interleukin-6 levels, and treatment with tocilizumab on top of dexamethasone was required. The present examination revealed Beau's lines which were associated with both prior COVID-19 infections.
Conclusions: Although nail changes look harmless, seeking Beau's lines during the physical examination might indicate past severe COVID-19 infection and a higher probability for reinfection and rehospitalisation.
References
Views: 355
HTML downloads: 57
PDF downloads: 199
Published:
2024-01-17
Issue:
2024: Vol 11 No 2
(view)










