Keywords
Hypereosinophilia, stroke, cytomegalovirus, Loeffer endocarditis
Abstract
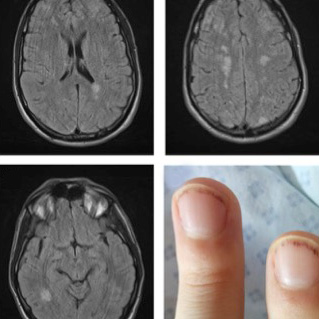
AFIP1L1-PDGFRA fusion can only be confirmed through molecular and cytogenetic investigations causing a delay in the diagnosis. However, patients with this mutation need urgent treatment because they present hypereosinophilia which may be associated with short-term tissue damage. Thromboembolism is a known cause of death in hypereosinophilic syndrome. A case of Loeffler endocarditis due to FIP1L1-PDGFRA-associated chronic eosinophilic leukemia presenting hemiparesis with fever, which also mislead the initial diagnosis, is reported.
References