Keywords
Pneumococcus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Fanconi syndrome, proximal renal tubulopathy
Abstract
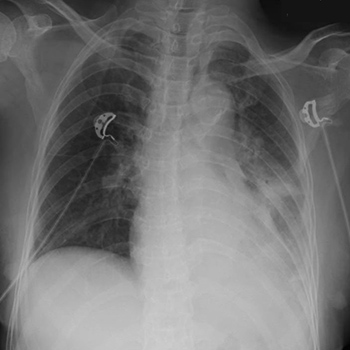
Acquired causes of Fanconi syndrome in adults are usually due to drugs, toxins or paraproteinaemias. Infectious causes are rarely described. We report a case of invasive pneumococcal disease in a patient who developed a Fanconi-like syndrome during the course of her illness. This patient presented with multiple electrolyte derangements consisting predominantly of hypokalaemia, hypomagnesaemia and hypophosphataemia during hospitalization for invasive pneumococcal disease with possible Austrian syndrome. Further evaluation revealed significant urinary losses of these electrolytes, uric acid and ?2-microglobulin. Together with evidence of hypouricaemia, this is suggestive of proximal renal tubulopathy, and hence a Fanconi-like syndrome. The patient’s clinical condition and biochemical anomalies improved following pneumococcus treatment.
References