Keywords
COVID-19, respiratory distress, phrenic paralysis, neurotropism
Abstract
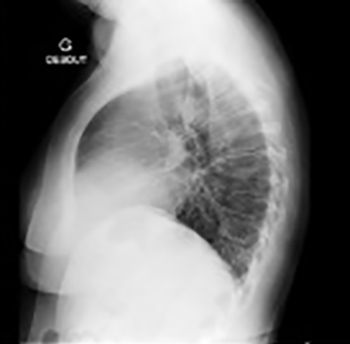
We describe an overweight COVID-19 patient with respiratory distress preceded by anosmia/dysgeusia with no lung injury shown on CT, angio-CT or ventilation/perfusion scans. Orthopnoea and paradoxical abdominal respiration were identified. Phrenic paralysis, demonstrated by examination of patient breathing, and on x-ray while standing breathing in and out, explained the respiratory distress. This is a rare and previously undescribed neurological complication of COVID-19 infection caused by vagus nerve injury.
References
Views: 1428
HTML downloads: 2447
PDF downloads: 613
Published:
2020-05-21
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 6
(view)










