Keywords
COVID-19, dissecting haematoma, dermatoporosis, coagulation abnormalities
Abstract
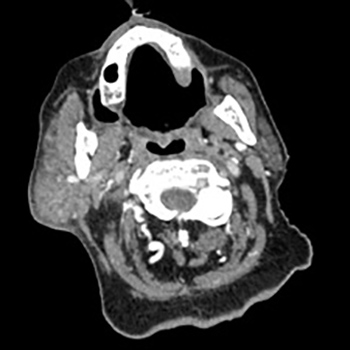
We describe the case of a patient hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure in a standard medical ward. During hospitalization, he was diagnosed with COVID-19 and transferred to a special unit. The clinical course was marked by worsening of the respiratory disease, the development of right parotiditis and thrombosis of the left internal jugular vein. Therapeutic anticoagulation was initiated and 2 days later, the minimal dermatoporosis lesions previously present in the upper extremities evolved to haemorrhagic bullae with intra-bullae blood clots and dissecting haematomas. Surgical management of the dissecting haematomas was difficult in the context of haemostasis abnormalities. The patient died 29 days after hospital admission.
References
Views: 1092
HTML downloads: 127
PDF downloads: 761
Published:
2020-06-12
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 7
(view)










