Keywords
Thrombocytosis, splenomegaly, hereditary spherocytosis, thrombosis, hypercoagulable
Abstract
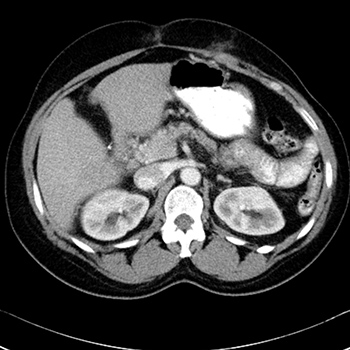
Reactive thrombocytosis after splenectomy is a feared cause of thrombosis throughout the arterial and venous system. There are many causes of splenomegaly, ranging from cirrhosis to lymphoma to hereditary spherocytosis. In this report, we will discuss a case of reactive thrombocytosis after splenectomy in a patient with hereditary spherocytosis. Splenomegaly is a relatively common finding in HD patients, causing extravascular haemolysis and thus leading to haemolytic anaemia. Splenectomy is usually considered when patients start to manifest severe symptoms such as abdominal pain, jaundice or worsening liver function tests. Our patient was a good surgical candidate and successfully underwent splenectomy but afterwards developed arterial and venous thrombosis due to reactive thrombocytosis. An extensive hypercoagulable work-up was unremarkable. The patient was started on hydroxyurea and anticoagulation with eventual improvement of platelet levels.
References
Views: 775
HTML downloads: 911
PDF downloads: 422
Published:
2021-07-06
Issue:
2021: Vol 8 No 7
(view)










