Keywords
Neurosyphilis, meningovascular syphilis, arteritis, stroke, acute cerebrovascular event
Abstract
Introduction: Neurosyphilis (NS) refers to a central nervous system infection caused by Treponema pallidum. In recent years, there has been an increasing incidence of syphilis; however, NS is uncommon compared to the era before the discovery of penicillin. Manifestations are usually non-specific, ranging from asymptomatic cases to syphilitic meningitis, meningovascular syphilis, general paresis and tabes dorsalis. Meningovascular syphilis can cause an inflammatory arteritis of cerebral arteries, leading to vascular occlusion and cerebral infarction.
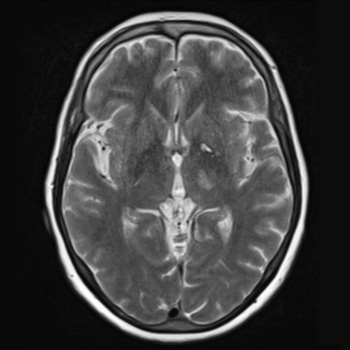
Case description: We report a case of an ischaemic stroke in a patient with several vascular risk factors, presenting with right hemiparesis, hemihypesthesia and dysarthria. Initial computed tomography with angiography of the head and neck was normal; however, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain revealed a thalamic and internal capsule infarct. Serum T. pallidum antibodies were positive, as well as a rapid plasma reagin test. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis confirmed the diagnosis of neurosyphilis, and the patient was treated with ceftriaxone for 14 days due to a penicillin allergy.
Discussion and conclusion: Although there is a high prevalence of stroke in patients with NS, this condition is typically underdiagnosed. Untreated NS carries a higher risk of stroke recurrence compared to other risk factors. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are essential. This case highlights the importance of considering NS in stroke victims, even in older patients with several additional vascular risk factors, to prevent recurrence and other complications.
References
Views: 350
HTML downloads: 49
PDF downloads: 261
Published:
2024-01-08
Issue:
2024: Vol 11 No 2
(view)










