Keywords
Rituximab, inflammatory myopathy, polymyositis, Behçet's disease, antiphospholipid syndrome
Abstract
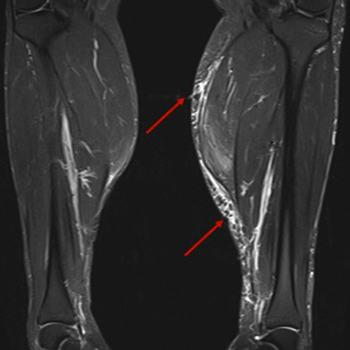
A 43-year-old Caucasian male initiated myalgias and loss of muscle strength in the upper and lower limbs, but especially at the shoulder and pelvic girdle. Creatinine phosphokinase was elevated seven-fold above the normal reference value and aldolase was slightly elevated. He had a previous diagnosis of Behçet's disease, antiphospholipid syndrome and hypertriglyceridaemia. At this time, he was on azathioprine 150 mg daily, colchicine 1 mg daily, warfarin and fenofibrate 200 mg daily. Fenofibrate was stopped and creatinine phosphokinase re-evaluated 2 months later, but it was higher, with persistent myalgias. By this time, prednisolone was restarted and the azathioprine dose reduced until it was discontinued. Nevertheless, 2 months after stopping azathioprine, the patient remained symptomatic and creatinine phosphokinase was persistently elevated. At this point, the authors requested myositis antibody testing to exclude overlap with a third autoimmune disorder, and Ro52 antibody was positive. Electromyography was normal. Magnetic resonance imaging of lower limb muscles was compatible with polymyositis. Muscular biopsy of the medial gastrocnemius revealed inflammatory myopathy. The authors proposed treatment with rituximab and after 3 months, the patient had clinically and analytically improved, with reduction of creatinine phosphokinase, without adverse reactions. As we can see in this case, rituximab could be a secure treatment for patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathy without improvement on glucocorticoids plus another immunosuppressive agent. This patient has a rare overlap syndrome, since this is the first case of an association between inflammatory myopathy, Behçet's disease and antiphospholipid syndrome described in the literature.
References
Views: 1173
HTML downloads: 120
PDF downloads: 546
Published:
2019-11-11
Issue:
Vol 6 No 11
(view)










