Keywords
Pneumocephalus, lumbar epidural anaesthesia, post-dural puncture headache
Abstract
Introduction: Lumbar epidural anaesthesia is a commonly used technique for analgesia during labour. One of the rare complications of this technique is pneumocephalus.
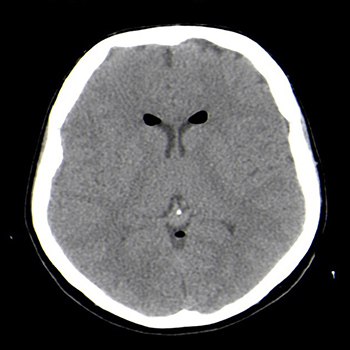
Case description: We report the case of a 35-year-old female admitted to the Emergency Department with severe headache associated with fast head movements. Five days previously she had a eutocic delivery and lumbar epidural anaesthesia was performed. A brain computed tomography (CT) scan showed pneumocephalus and she was admitted to the hospital ward. A brain CT scan on the fourth day of hospitalization showed resolution of ventricular pneumocephalus.
Discussion: The most frequently occurring symptom with pneumocephalus is headache associated with fast brain motion resulting from air injection and meningeal irritation. When there is clinical suspicion of pneumocephalus, a brain CT scan should be performed for the diagnosis.
References
Views: 920
HTML downloads: 169
PDF downloads: 422
Published:
2020-01-22
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 2
(view)










