Keywords
Ponatinib, acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, Philadelphia chromosome-positive, ARDS, pneumonitis
Abstract
Ponatinib is a third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that can effectively treat patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), particularly those with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+ALL) subtype, who are resistant or have previously received other TKIs.
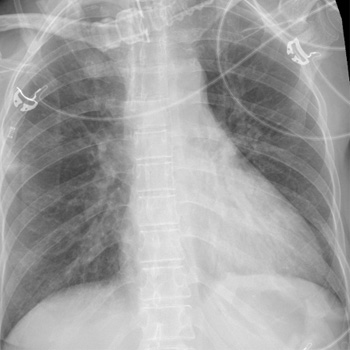
We report a case of a 42-year-old female with Ph+ALL who was admitted to the intensive care unit with respiratory failure and severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), while on treatment with ponatinib. Despite being treated with multiple antibiotics and antivirals, the patient’s condition continued to worsen, and pulmonary complications secondary to TKI were suspected. After starting a steroid regimen, the patient’s condition improved drastically with resolution of the pulmonary complications.
While many adverse events (AEs) happen in the beginning stages of TKI treatment, certain toxicities may not arise until months after therapy initiation. Cardiovascular complications are the most common AE of ponatinib, including heart failure and arterial hypertension. Pulmonary complications may occur, and management includes drug cessation and individualised steroid therapy.
In case of respiratory failure without signs of infection and no improvement with antimicrobial treatment, clinicians should consider the possibility of pulmonary toxicity associated with ponatinib.
References
Views: 461
HTML downloads: 46
PDF downloads: 344
Published:
2023-11-13
Issue:
2023: Vol 10 No 12
(view)










