Keywords
COVID-19, POCUS, B lines, flashing phenomenon, pulmonary embolism
Abstract
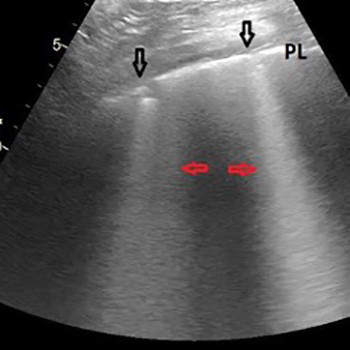
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and the World Health Organization (WHO) declared it a pandemic on 11 March 2020. Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is a real-time bedside tool used by physicians to guide rapid, focused and accurate evaluation in order to identify or rule out various pathologies. We describe the case of an elderly man who had fallen at home 3 days previously and was hypoxic at presentation to the emergency department (ED). POCUS in the ED helped to identify a combination of lung and vascular involvement that indicated COVID-19 infection, which was confirmed by a laboratory test.
References