Keywords
L-asparaginase, hypertriglyceridemia, pancreatitis, plasmapheresis
Abstract
L-asparaginase is used for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Hypertriglyceridaemia is a side effect and associated with potentially fatal complications, including acute pancreatitis. Plasmapheresis may have a role in treatment when triglycerides are >2000 mg/dl.
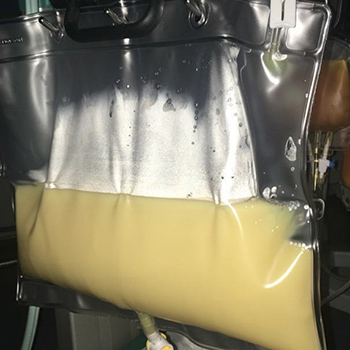
We report the case of a 39-year-old woman treated with L-asparaginase for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, who developed severe hypertriglyceridaemia (6560 mg/dl) and acute pancreatitis. Intravenous insulin infusion was started, along with fenofibrate and atorvastatin administration, and platelet transfusion. Plasmapheresis was carried out leading to a frank decline in serum triglyceride levels (366 mg/dl), a decrease in pancreatic enzymes and clinical improvement.
The diagnosis of pancreatitis secondary to L-asparaginase should lead to immediate drug withdrawal, and plasmapheresis should be considered when serum triglyceride values exceed 2000 mg/dl. In our case, there was a 95% triglyceride removal rate. This response illustrates the strong effectiveness of early treatment with plasmapheresis in severe and symptomatic hypertriglyceridaemia associated with L-asparaginase.
References