Keywords
Livedoid vasculopathy, peripheral neuropathy, pain management
Abstract
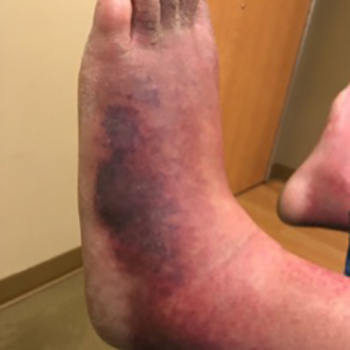
Livedoid vasculopathy (LV) is a rare clinical condition presenting as painful lesions mostly on the lower extremities. We present a case of LV with peripheral neuropathy in a young man initially misdiagnosed and treated for cellulitis. He was started on aspirin, pentoxifylline and apixaban immediately after the diagnosis of LV. However, pain management was a real challenge for the clinicians. Hence, he was later treated with epoprostenol and amlodipine for vasodilation, steroids for any possible inflammation, and antibiotics to treat superimposed infection. Irrespective of all the above, his pain was uncontrollable, and he finally received ketamine infusions along with narcotics, achieving better pain control. Various studies support the use of intravenous immunoglobulin and anti-TNF agents for pain relief in idiopathic and secondary LV. Intermittent low-dose dabigatran has also been found to be effective in the maintenance of remission in LV. However, no large studies have yet been conducted to confirm the efficacy of these medications.
References
Views: 447
HTML downloads: 183
PDF downloads: 410
Published:
2023-02-03
Issue:
2023: Vol 10 No 1
(view)










