Keywords
Purpura fulminans, sepsis, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
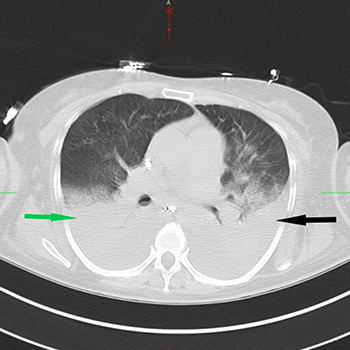
Infectious purpura fulminans (PF) is a rare presentation of disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC) due to diffuse intravascular thrombosis and haemorrhagic infarction of the skin. PF can present in infancy/childhood or adulthood and usually presents as ecchymotic skin lesions, fever and hypotension. It is most commonly a consequence of sepsis related to Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae. Despite aggressive management of sepsis with intravenous fluids, antibiotics, and conventional and nonconventional therapies, the condition still carries a mortality rate of 43%[1]. Streptococcus pneumoniae mostly presents with community-acquired pneumonia. We present a case of PF secondary to DIC related to Pneumococcal sepsis in an otherwise healthy and immunocompetent patient.
References
Views: 1368
HTML downloads: 592
PDF downloads: 596
Published:
2019-12-30
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 1
(view)










